Proximity sensors are used to identify the presence of the material using EMF, light, or sound. They are nothing but the detectors. The proximity sensor checks if an object is present in the specified area, if yes, it then sends signals.
There are many types, depending on the applications and environments we can use one of them. The basic principle of working will be similar independent of the type.
There are many types, depending on the applications and environments we can use one of them. The basic principle of working will be similar independent of the type.
Operating principle of a proximity sensor
A proximity sensor is used for contact or non-contact type of detection of objects.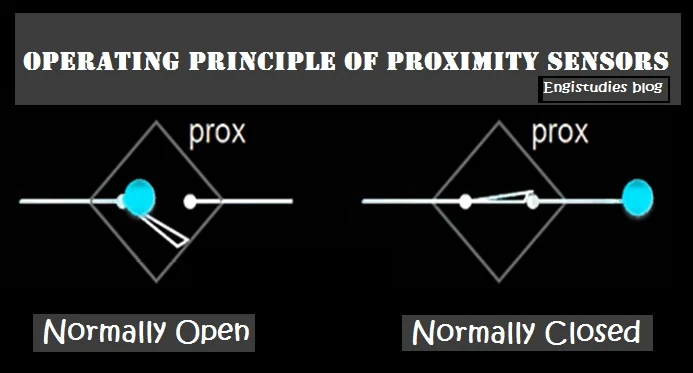 |
| Operating principle |
Construction
The construction includes the following basic parts.- An oscillator
- A core
- A detector circuit
- An output circuit
Many more parts are used in the construction but I have listed only the basic parts.
Working
The working principle can be described as below,- A proximity sensor generates a signal in the form of a sin wave of fixe frequency.
- The coil is then powered by this signal.
- The coil in conjunction with ferrite core induces an electromagnetic field.
- When an object cuts the field, the oscillator voltage gets reduced.
- This reduction in voltage depends on the distance of the object from the sensor. The detecting circuit detects this fluctuated voltage.
- You can find two configurations viz. Normally-open and Normally-closed. If the sensor has a normally open configuration, its output signal will be an on-signal and vice-versa.
We can classify, according to sensing technology used, as below:
Please note that at present sensors comes with different configurations like, AC or DC, NO or NC, with fixed sensing range or adjustable sensing range. You will also choose from various the physical configurations such as shielded/non-shielded, metal/plastic body, round/rectangular/fork shaped, and 2/3/4 wire connectors.
Inductive sensor
The inductive sensor works on Faraday's law of induction. It detects the object without touching or disturbing it. It can detect metal objects. The sensing range depends upon the type of material of the object being targeted.
Most of the inductive sensors come with a range less than 6cm.
Most of the inductive sensors come with a range less than 6cm.
Capacitive sensor
Capacitive sensor can detect metallic object along with it can also detect wood, liquids, powders, etc. Capacitive sensors nowadays replaced the use of mechanical push buttons. 25 mm is the maximum sensing range for most of the capacitive sensors.
Read: Differences Between Truss and Frame
Read: Differences Between Truss and Frame
Photoelectric sensor
Photoelectric sensors are light sensitive elements. The object is not touched while detecting. They consist of an emitter and a receiver.
They are further classified as:
They are further classified as:
- Direct Reflection (Diffused)
- Reflection with Reflector (Retro-reflective)
- Thru-Beam
Magnetic sensor
Magnetic sensors are used to identify magnets.The highest sensing range is 120 mm.
It is actuated in the presence of a permanent magnet.
It is actuated in the presence of a permanent magnet.
Ultrasonic sensor
The ultrasonic sensor uses sound waves for detection. It is used to detect the total distance range between the sensor and object. It uses a single ultrasonic element for both emission and reception. The temperature and humidity of the air affect the accuracy of the sensor.
What is the use of a proximity sensor?
The proximity sensors are used in lots of different fields.- In car bumpers to detect the safe parking distance.
- Packaging machines and conveyors use sensors to position bottles, cans, and similar items.
- Mobile devices and computers in the form of touch screens and special sensors.
- Inductive sensor is used to sense high-speed applications.











No comments:
Post a Comment